
Icon Cancer Centre Facebook Live: Lung Cancer
The human body is made up of billions of cells, which in a healthy body are usually turning over slowly, in an organised way.
Cancer is the term we use for a disease that occurs when these cells grow in an abnormal and uncontrolled way. This uncontrolled growth of cells can cause a lump or a mass to form, which is called a tumour. Tumours can be benign or malignant.
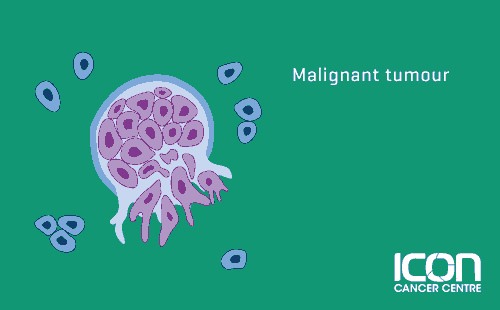
These tumours are made up of cancer cells. They are usually faster growing, can destroy tissue and have the ability to spread to other parts of the body.
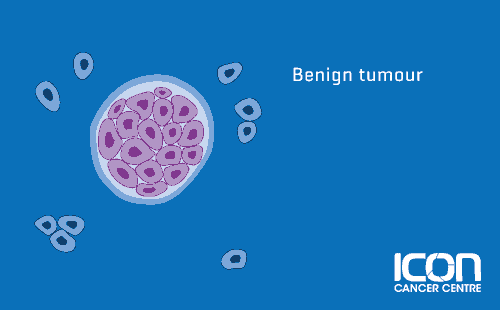
These tumours usually grow slowly and do not spread to other parts of the body. Benign tumours only become a problem if they grow very large, taking up space and affecting the way the body works.
Cancer may also affect blood cells, causing blood cancers such as leukaemia, lymphoma or myeloma. These blood cancers also cause normal blood cell production to be reduced due to the uncontrolled growth of the abnormal (malignant) cells in the bone marrow.
Over time, the uncontrolled growth of cancer cells usually becomes too much for the body to cope with, or will spread to a part of the body that is essential for life.
Oncology is the branch of medicine that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment and research of cancer.
This includes medical oncology, radiation oncology, haematology and surgical oncology.
An oncologist is a doctor that specialises in treating cancer. Oncologists support patients from diagnosis, through treatment and into survivorship as part of a multidisciplinary team. While some oncologists specialise in certain types of cancer (e.g. breast cancer), others treat a wide range of different cancer types. Oncologists also conduct research into cancer to improve our understanding of the disease and its treatment.
We cover essential terminology used throughout each stage of your journey, including treatment terms, medical procedures, common side effects, and more.

Doctors who specialise in treating cancer using radiation therapy.
Doctors who specialise in diagnosing and treating solid tumours (e.g. cancerous tumours in the lung, breast or bowel) with the use of chemotherapy drugs, immunotherapy and hormone therapies.
Doctors who specialise in treating cancers affecting the blood/bone marrow (e.g. leukaemia) and lymphatic system (i.e. lymphoma), and often perform bone marrow transplants.
Doctors who specialise in removing cancerous tissue through surgery.
The content on the Bowen Icon Cancer Centre website is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. It is not a substitute for consultation with a qualified medical practitioner. For personalised medical guidance, please consult with your GP or another qualified healthcare provider.

Discover our comprehensive collection of content designed to inform, support, and guide you through every aspect of cancer care. From the latest news and updates to personal patient experiences and educational resources, these materials provide valuable insights to help you better understand cancer, treatment options, and the journey ahead.