Quick facts about ovarian cancer
The average age of women when they are diagnosed with ovarian cancer is 64 years old
Anyone with ovaries can get ovarian cancer, so it mostly affects women. Transgender men and intersex people can also get ovarian cancer if they have ovaries
Types of ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer can be one of three types:
-
Epithelial ovarian cancer
This can involve either one or both ovaries, where cancer cells grow on the outside of the ovary. This type of ovarian cancer is the most common form, accounting for approximately 90% of ovarian cancers.
-
Germ cell ovarian cancer
This involves the cells that produce the eggs and accounts for approximately 4% of all ovarian cancers.
-
Stromal tumour ovarian cancer
This involves the tissues that support the ovary in producing oestrogen and progesterone hormones. This type of ovarian cancer is very rare.
Signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer
As signs and symptoms for ovarian cancer can be similar to other common conditions, it’s important to see your GP or healthcare professional if you experience any of the symptoms below. Discussing anything concerning as soon as possible can help give you peace of mind and offer the best chance of successful treatment if you receive an ovarian cancer diagnosis.
Symptoms may include:

Pain in the abdomen or pelvic area

Bloating or an extended abdomen

Bleeding between periods or after menopause

Reduced appetite or a feeling of being full after small meals

Weight gain or loss that can’t be explained by diet and exercise-related factors

Changes in urinating, including increase in frequency and urgent need to pass urine

Changes in bowel habits such as constipation or diarrhoea

Tiredness
Stages of ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is typically staged using the FIGO (International Federation of Gynaecology and Obstetrics) system, which helps define what your cancer looks like.
Within each stage of ovarian cancer, there are sub-stages listed from A through to D which describe the extent of the tumour.
The FIGO system, along with other tests, helps determine the stage of your ovarian cancer using the guidelines below:
-
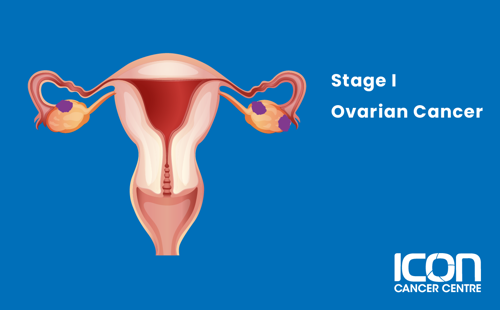
Stage I
Cancer has been found in either one or both ovaries.
-
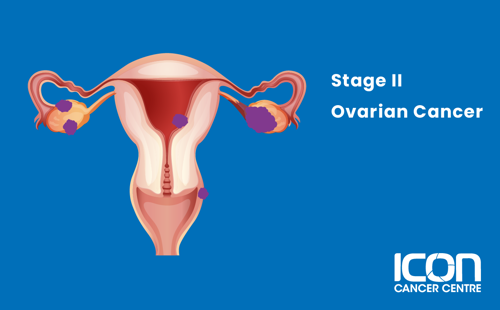
Stage II
The cancer has spread beyond one or both ovaries to other nearby organs such as the uterus or bladder.
-
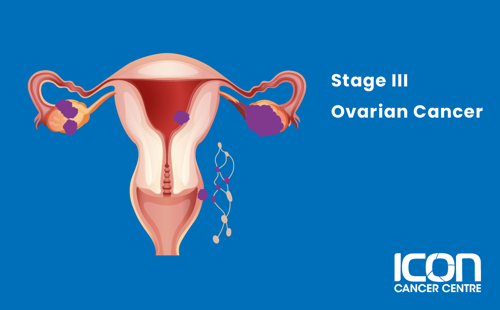
Stage III
The cancer has spread beyond the ovaries and nearby organs to the lining of the abdomen or lymph nodes.
-
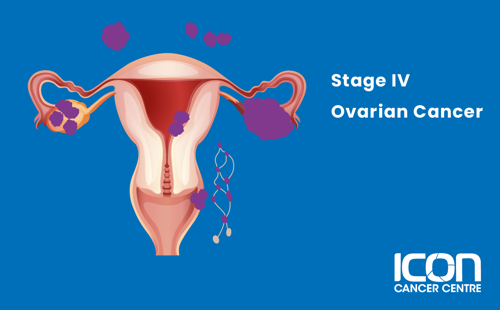
Stage IV
The cancer has spread to other areas of the body such as the lung.
Treatment for ovarian cancer
There are many different types of treatment for ovarian cancer. Your treatment will depend on you and your cancer.




